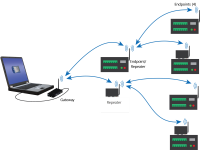
Computer-to-RF network with parallel repeaters (using SubNet ID)
In this example, the gateway radio is connected to a computer running LoggerNet. One stand-alone repeater (Repeater 1) is used to access several endpoint radios connected to data loggers in the field. The stand-alone repeater consists of an RF451/RF452, power supply, and antenna. Another repeater (endpoint/repeater) connected to a data logger is used to access several other endpoint radios on data loggers.
To take advantage of the low power mode, those devices that are NOT repeaters should be configured as endpoints and not as endpoint/repeaters. In this configuration, it may be desirable to use an external omnidirectional antenna at the repeaters.
A maximum of four repeaters are allowed in a network. When a repeater is used, the RF throughput is cut in half. Throughput is the rate at which data is sent or received. Reducing throughput means less data can be transmitted in a specified amount of time.
Remember, each data logger must have a unique PakBus address.
The Radio ID setting allows a transceiver to be designated an arbitrary, user-selectable, 4-digit number which identifies the transceiver in diagnostics mode. When used in conjunction with PakBus data loggers, we recommend this setting be assigned the PakBus address of the station. This is because the Radio ID appears in the Network Diagnostics application within the FreeWave Tool Suite software, and it allows the user to associate a particular data logger with its attached radio.