StdDevRun (Running Standard Deviation)
The StdDevRun instruction is used to output the running standard deviation of a measurement.
Syntax
StdDevRun ( Dest, Reps, Source, Number, RunReset [optional] , Count [optional] TotalCalls [optional], Call_ID [optional], StdDevType [optional])
The following simple program shows the use of the AvgRun,TotalRun, MinRun, MaxRun, and StdDevRun instructions. A running value (running average, running total, running minimum, running maximum, and running standard deviation) of a counter is kept over 9 values. If the Reset variable is set to true (for example, toggled 'true' via Numeric Monitor), then AvgRun, TotalRun, MinRun, MaxRun, and StdDevRun all return the same value (the current value), because the history over which the running value is calculated is cleared. Note that once Reset = True, it must be manually or programmatically toggled back off (False). When Reset is toggled off (False), then calculation of the running value resumes, beginning with the current input. Note that until the data logger has taken N measurements (in this case N=9) the running value is based on the actual number of measurements made.
Public Counter As Long, Reset As Boolean, Run_Avg,Run_Min,Run_Max,Run_Total, Run_StdDev
'Main Program
BeginProg
Reset = false
Scan (1,Sec,0,0)
counter = counter + 1
AvgRun (Run_Avg,1,counter,9,Reset) 'Running average of last 9 values
TotalRun
(Run_Total,1,counter,9,Reset)'Running total of last 9 values
MinRun (Run_Min,1,counter,9,Reset)'Running minimum of last 9
values
MaxRun (Run_Max,1,counter,9,Reset)'Running maximum of last 9 values
StdDevRun (Run_StdDev,1,counter,9,Reset)'Running standard deviation of last 9 values
NextScan
EndProg
OPTIONAL TOTALCALLS AND CALL_ID EXAMPLE
The following program demonstrates using the optional parameters TotalCalls and Call_ID to calculate running standard deviations for 3 source variables, X, Y, and Z in a subroutine.
Public X As Float
Const X_ID = 1
Public Y As Float
Const Y_ID = 2
Public Z As Float
Const Z_ID = 3
Public X_stddev_sub
Public Y_stddev_sub
Public Z_stddev_sub
Public Reset_Runs As Boolean = false
Dim N as Long
Sub run(ResultStdDevRun As Float, source As Float, sourceID)
'StdDevRun ( Dest, Reps, Source, Number, RunReset [optional] , Count [optional] TotalCalls [optional], Call_ID [optional], StdDevType [optional])
StdDevRun (ResultStdDevRun,1,source,10,Reset_Runs,N,3, sourceID) 'TotalCalls = 3
EndSub
'Main Program
BeginProg
Scan (1,Sec,0,0)
X += 1 'generate some data for the source variables for demonstration
Y += 2
Z += .25
'Call subroutine 3 times (once for each source variable)
Call run(X_stddev_sub,X,X_ID)
Call run(Y_stddev_sub,Y,Y_ID)
Call run(Z_stddev_sub,Z,Z_ID)
NextScan
EndProg
OPTIONAL Sample Standard Deviation EXAMPLE
A sample standard deviation is supported OS
Public Counter As Long,
Public Run_StdDev
Dim N as Long
'Main Program
BeginProg
Scan (1,Sec,0,0)
Counter = Counter + 1
'StdDevRun ( Dest, Reps, Source, Number, RunReset [optional] , Count [optional] TotalCalls [optional], Call_ID [optional], StdDevType [optional])
StdDevRun (Run_StdDev,1,Counter,100,False)'Running population standard deviation of last 100 values
StdDevRun (Run_StdDev,1,Counter,100,False,N,1,1,1)'Set StdDveType = 1 to get sample standard deviation of last 100 values
NextScan
EndProg
Remarks
This instruction, when used, must appear between the Scan … NextScan instructions. A running standard deviation is the standard deviation of the last N values where N is specified in the Number argument. Until the data logger has taken N measurements the standard deviation is calculated based on the number of actual measurements made.
The running standard deviation is calculated from the non-![]() NAN Not a number. A data word indicating a measurement or processing error. Voltage overrange, SDI-12 sensor error, and undefined mathematical results can produce NAN. values in the buffer of historical data. In the event that all values in the buffer are NAN, the output will be 0. The StdDevRun instruction should be called conditionally (only when good values are received) to avoid NAN values affecting the output. When called conditionally, the standard deviation is calculated as the standard deviation of the last number of good values.
NAN Not a number. A data word indicating a measurement or processing error. Voltage overrange, SDI-12 sensor error, and undefined mathematical results can produce NAN. values in the buffer of historical data. In the event that all values in the buffer are NAN, the output will be 0. The StdDevRun instruction should be called conditionally (only when good values are received) to avoid NAN values affecting the output. When called conditionally, the standard deviation is calculated as the standard deviation of the last number of good values.
Parameters
Dest (Destination)
The Variable in which to store the results of the instruction. Right-click the parameter to display a list of defined variables.
If this instruction has a Repetitions parameter and it is greater than 1, the results are stored in an array with the variable name. The array must be dimensioned large enough to hold all of the values returned from all of the Reps.
Type: Variable or Array
Reps (Repetitions)
The number of repetitions for the measurement or instruction.
Type: Constant integer (or expression that evaluates as a constant).
For the StdDevRun instruction, the Reps parameter is the number of variables in the array for which a running standard deviation should be calculated. When the Source is not an array, or only a single variable in the array should be used, Reps should be 1.
Source
The name of the Variable that is the input for the instruction. Right-click the parameter to display a list of defined variables.
Type: Variable
Number
The number of values of Source to be used for calculating the running average, running total, running minimum, running maximum, or running standard deviation.
Type: Constant (or expression that evaluates as a constant)
Optional Parameters
RunReset
When RunReset is true, the history over which the running value (for example, running average, running maximum, running minimum, running total, or running standard deviation) is calculated is cleared, so that the value returned is calculated from a a single value, the current input. Note that the reset parameter does not automatically toggle back to false once set to true. When the reset parameter is set back to false (problematically or manually), then the running average, running maximum, running minimum, or running total continues, starting with the current input. Note that until the data logger has taken N measurements, the running average/total/maximum/minimum is calculated based on the actual number of measurements made since reset was set back to false.
Type: ![]() Boolean Data type used to represent conditions or hardware that have only two states (true or false) such as flags and control ports. variable or expression that evaluates true/false
Boolean Data type used to represent conditions or hardware that have only two states (true or false) such as flags and control ports. variable or expression that evaluates true/false
The TotalCalls and Call_ID optional parameters below, allow a single instance of the instruction (AvgRun, MaxRun, MinRun, StdDevRun) to be called with different source variables, as in a subroutine or function. Click here for additional information. These parameters are available with operating system
TotalCalls
Optional parameter that specifies the total number of calls to a specific instance of the instruction (AvgRun, MaxRun, MinRun, StdDevRun) in the program.
Type: Constant integer
Call_ID
Specifies a unique ID number for each specific call of the instruction.
Type: Integer
NOTE: If more than one instance of the instruction occurs in the program, each instance requires its own set of TotalCalls and Call_ID parameters.
Count
Optional parameter
StdDevType
Optional parameter added in OS
The following equation is used to calculate the default, population StdDev:
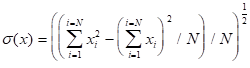
In contrast, the formula for the sample standard deviation is:
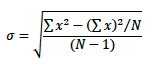
Note: the preceding optional parameters (RunReset, Count, TotalCall, and Call_ID) must be set in order to use the StdDevType option. The Reset parameter should be 0 (false), Count (N), should be a variable destination,TotalCall is 1, and Call_ID is any user-specified integer. See TotalCalls Call_ID for more information.See the Sample Standard Deviation example program for correct syntax.
NOTE: This instruction uses ![]() high precision math A normal single precision float has 24 bits of mantissa. With high precision, a 32 bit extension of the mantissa is saved and used internally, resulting in 56 bits of precision. Instructions that use high precision are Average, AvgRun, AvgSpa, CovSpa, MovePrecise, RMSSpa, StdDev, StdDevSpa, TotalRun, and Totalize.. A normal single precision float has 24 bits of mantissa. With high precision, a 32 bit extension of the mantissa is saved and used internally, resulting in 56 bits of precision. Instructions that use high precision are
high precision math A normal single precision float has 24 bits of mantissa. With high precision, a 32 bit extension of the mantissa is saved and used internally, resulting in 56 bits of precision. Instructions that use high precision are Average, AvgRun, AvgSpa, CovSpa, MovePrecise, RMSSpa, StdDev, StdDevSpa, TotalRun, and Totalize.. A normal single precision float has 24 bits of mantissa. With high precision, a 32 bit extension of the mantissa is saved and used internally, resulting in 56 bits of precision. Instructions that use high precision are