Device Configuration Utility Security Check
A Security Check is provided through Device Configuration Utility, starting with version 2.29. This check helps you identify areas where security can be improved.
All suggestions shown in Device Configuration Utility are optional and no changes will be made unless you make them. For example, Device Configuration Utility uses a simple set of criteria to suggest a strong password. If you have your own criteria, you can use it. Because every deployment can be different, Device Configuration Utility will provide you with the information you need to ensure your data logger security is optimized for your application.
In general, green, blue, and red icons indicate password strength.
- Green: strong password
- Blue: weak password
- Red: no password set
A strong password has the following:
- Eight or more characters
- One upper case letter
- One lower case letter
- One digit
- One special character
The green, blue, and red icons may also show the potential severity of a security vulnerability.
- Green: good, no action needed
- Blue: advisory information
- Red: action recommended
PakBus
![]() PakBus ® A proprietary communications protocol developed by Campbell Scientific to facilitate communications between Campbell Scientific devices. Similar in concept to IP (Internet Protocol), PakBus is a packet-switched network protocol with routing capabilities. A registered trademark of Campbell Scientific, Inc. encryption is the best data logger option to secure PakBus communications. For data loggers that have a UID, PakBus Encryption is enabled by default. The default PakBus Encryption Key is the UID.The PakBus Encryption (AES-128) Key can be changed or cleared (deleted) in Device Configuration Utility.
PakBus ® A proprietary communications protocol developed by Campbell Scientific to facilitate communications between Campbell Scientific devices. Similar in concept to IP (Internet Protocol), PakBus is a packet-switched network protocol with routing capabilities. A registered trademark of Campbell Scientific, Inc. encryption is the best data logger option to secure PakBus communications. For data loggers that have a UID, PakBus Encryption is enabled by default. The default PakBus Encryption Key is the UID.The PakBus Encryption (AES-128) Key can be changed or cleared (deleted) in Device Configuration Utility.
Passwords may be changed from the default UID. However, when the data logger is reset to factory defaults or a new OS is sent, the default password will revert to the UID.
A PakBus Encryption Key forces PakBus data to be encrypted during transmission. The Security Check will check if the data logger has a PakBus Encryption Key set and a PakBus/TCP Password.
When neither of these is set, the Security Check will indicate that action is recommended.
The Security Check will not suggest setting a PakBus/TCP password if PakBus Encryption is already enabled. However, a PakBus/TCP password can be used with PakBus encryption.
Web services
The Security Check will check to see if ![]() HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol. A TCP/IP application protocol. or
HTTP Hypertext Transfer Protocol. A TCP/IP application protocol. or ![]() HTTPS Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. A secure version of HTTP. is enabled. If these protocols are not being used but are enabled, we recommend disabling them.
HTTPS Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. A secure version of HTTP. is enabled. If these protocols are not being used but are enabled, we recommend disabling them.
HTTP
Anonymous HTTP access is disabled by default. HTTP will be accessible with admin as the username and UID as the admin password.
Passwords may be changed from the default UID. However, when the data logger is reset to factory defaults or a new OS is sent, the default password will revert to the UID.
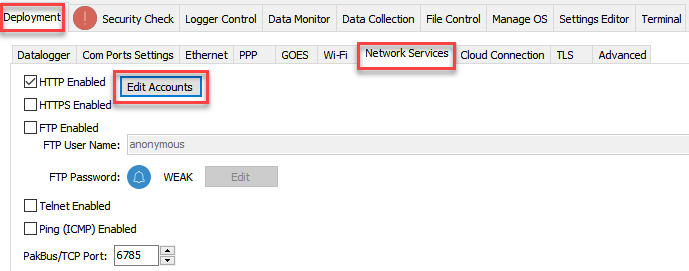
HTTP is an insecure protocol and can allow access to data logger data, settings, and programming. HTTP should only be enabled if it is required, and the data logger is on a secure network. If the data logger is not using web API or a hosted web page, then HTTP should be disabled. If HTTP protocol is used, user accounts should be configured with user names and passwords. See Device Configuration Utility > Deployment > Network Services > Edit Accounts to make changes.
See Web interface for more information.
HTTPS
HTTPS is a secure protocol, but it is disabled by default. It should only be enabled if necessary, as it grants access to data logger data, settings, and programming. If the data logger is not using web API or a hosted web page, then HTTPS should be disabled. If you do enable HTTPS, ensure that user accounts are also set up for security. Expect delays when using HTTPS, especially when first connecting.
Network services
The Security Check will check to see if any of the following network services are enabled. These services can be used to discover your data logger on an IP network. See Device Configuration Utility > Deployment > Network Services tab, to make changes.
FTP, Telnet, and Ping services are disabled by default.
FTP
![]() FTP File Transfer Protocol. A TCP/IP application protocol. is an insecure protocol that allows access to data logger data and files. FTP is disabled by default. However, when enabled, the UID will be the default FTP password.
FTP File Transfer Protocol. A TCP/IP application protocol. is an insecure protocol that allows access to data logger data and files. FTP is disabled by default. However, when enabled, the UID will be the default FTP password.
Passwords may be changed from the default UID. However, when the data logger is reset to factory defaults or a new OS is sent, the default password will revert to the UID.
FTP should only be enabled if it is required. If the FTP file transfer is not needed, then FTP should be disabled. Some data loggers support using SFTP (only as a client); this can improve file transfer security. Consider using a public/private key pair for SFTP authentication. Load a .PEM format file through the Device Configuration Utility Settings Editor > Advanced tab.
-
Maximum key file size: 4 KB public, 4 KB private
-
Key exchange methods:
-
ecdh-sha2-nistp256
-
ecdh-sha2-nistp384
-
ecdh-sha2-nistp521
-
diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha256
-
diffie-hellman-group16-sha512
-
diffie-hellman-group18-sha512
-
diffie-hellman-group14-sha256
-
diffie-hellman-group14-sha1
-
diffie-hellman-group1-sha1
-
diffie-hellman-group-exchange-sha1
-
-
Host key types:
-
ecdsa-sha2-nistp256
-
ecdsa-sha2-nistp384
-
ecdsa-sha2-nistp521
-
ecdsa-sha2-nistp256-cert-v01@openssh.com
-
ecdsa-sha2-nistp384-cert-v01@openssh.com
-
ecdsa-sha2-nistp521-cert-v01@openssh.com
-
rsa-sha2-512
-
rsa-sha2-256
-
ssh-rsa
-
ssh-rsa-cert-v01@openssh.com
-
-
Supported ciphers:
-
aes256-ctr
-
aes192-ctr
-
aes128-ctr
-
aes256-cbc
-
aes192-cbc
-
aes128-cbc
-
For more information, see How to Generate SFTP Keys Easily ![]() .
.
Telnet
![]() Telnet A software utility that attempts to contact and interrogate another specific device in a network. Telnet is resident in Windows OS., disabled by default, is an insecure protocol. It should only be enabled if it is required, and the data logger is on a secure network. PakBus is the preferred way of accessing the data logger terminal interface.
Telnet A software utility that attempts to contact and interrogate another specific device in a network. Telnet is resident in Windows OS., disabled by default, is an insecure protocol. It should only be enabled if it is required, and the data logger is on a secure network. PakBus is the preferred way of accessing the data logger terminal interface.
Ping
![]() Ping A software utility that attempts to contact another device in a network., disabled by default, makes the data logger visible to network scans. It should only be enabled if it is required.
Ping A software utility that attempts to contact another device in a network., disabled by default, makes the data logger visible to network scans. It should only be enabled if it is required.
Operating System Status
The Security Check will check to see if your data logger is running the latest operating system. Newer operating systems may have enhanced security measures. See Updating the operating system for more information.