General serial communications
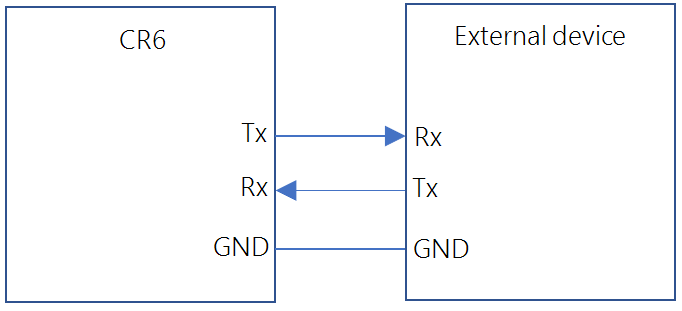
The data logger supports two-way serial communications. These communications ports can be used with smart sensors that deliver measurement data through serial-data protocols, or with devices such as modems, that communicate using serial data protocols.
![]() CRBasic Campbell Scientific's BASIC-like programming language that supports analog and digital measurements, data processing and analysis routines, hardware control, and many communications protocols. instructions for general serial communications include:
CRBasic Campbell Scientific's BASIC-like programming language that supports analog and digital measurements, data processing and analysis routines, hardware control, and many communications protocols. instructions for general serial communications include:
|
|
See this application note for more information on interfacing serial sensors with Campbell Scientific data loggers: Serial Sensors | Interfacing with CS Data Loggers ![]() .
.
See the CRBasic Editor help for detailed instruction information and program examples: ![]()
To communicate over a serial port, it is important to be familiar with the protocol used by the device with which you will be communicating. Refer to the manual of the sensor or device to find its protocol and then select the appropriate options for each CRBasic parameter. See the application note Interfacing Serial Sensors with Campbell Scientific Dataloggers ![]() for more programming details and examples.
for more programming details and examples.
Configure C or U terminals as serial ports using ![]() Device Configuration Utility Software tool used to set up data loggers and peripherals, and to configure PakBus settings before those devices are deployed in the field and/or added to networks. Also called DevConfig. or by using the
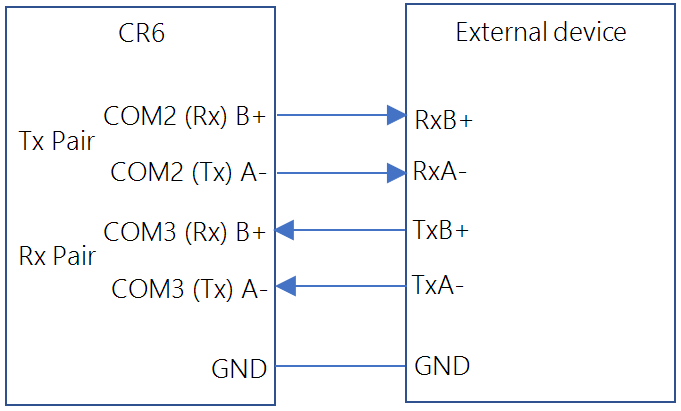
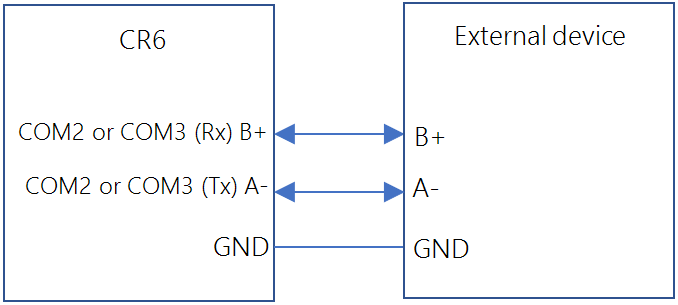
Device Configuration Utility Software tool used to set up data loggers and peripherals, and to configure PakBus settings before those devices are deployed in the field and/or added to networks. Also called DevConfig. or by using the SerialOpen() CRBasic instruction. C and U terminals are configured in pairs for TTL and LVTTL communications, and C terminals are configured in pairs for RS-232 or half-duplex RS-422 and RS-485. All four C terminals are required for full-duplex RS-422.
|
Serial communications summary |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
RS-232 |
RS-485 |
RS-422 |
TTL |
LVTTL |
TTL-INV |
LVTTL-INV |
|
Communications |
Point-to-point |
Multi-drop |
Single ended Multi-drop |
Point-to-point |
Point-to-point |
Point-to-point |
Point-to-point |
|
Maximum number of devices |
1 Transmitter 1 Receiver |
32 Transmitters 32 Receivers |
1 Transmitter 10 Receivers |
1 Tx 1 Rx |
1 Tx 1 Rx |
1 Tx 1 Rx |
1 Tx 1 Rx |
|
Mode type |
Full duplex |
Full duplex Half duplex |
Full duplex Half duplex |
Full duplex |
Full duplex |
Full duplex |
Full duplex |
|
Reference |
Single wire Tx ref to GND |
Differential pair TxB+ referenced to TxA– |
Single wire Tx referenced to GND |
||||
|
Voltage range |
–25 V to 25 V |
–5 V to 5 V |
–6 V to 6 V |
0 V to 5 V |
0 V to 3.3 V |
0 V to 5 V |
0 V to 3.3 V |
|
Idle voltage |
–25 V to |
–0.2 V to 5 V |
–0.2 V to 6 V |
5 V |
3.3 V |
0 V |
0 V |