Electrostatic discharge and lightning protection
Lightning strikes may damage or destroy the data logger, associated sensors and power supplies.
Electrostatic discharge (![]() ESD Electrostatic discharge.) can originate from several sources, the most common and destructive are primary and secondary lightning strikes. Primary lightning strikes hit instrumentation directly. Secondary strikes induce voltage in power lines or wires connected to instrumentation. While elaborate, expensive, and nearly infallible lightning protection systems are on the market, Campbell Scientific, for many years, has employed a simple and inexpensive design that protects most systems in most circumstances. The system consists of a lightning rod, metal mast, heavy-gauge ground wire, and ground rod to direct damaging current away from the data logger. This system, however, is not infallible. The following image displays a typical application of the system:
ESD Electrostatic discharge.) can originate from several sources, the most common and destructive are primary and secondary lightning strikes. Primary lightning strikes hit instrumentation directly. Secondary strikes induce voltage in power lines or wires connected to instrumentation. While elaborate, expensive, and nearly infallible lightning protection systems are on the market, Campbell Scientific, for many years, has employed a simple and inexpensive design that protects most systems in most circumstances. The system consists of a lightning rod, metal mast, heavy-gauge ground wire, and ground rod to direct damaging current away from the data logger. This system, however, is not infallible. The following image displays a typical application of the system:
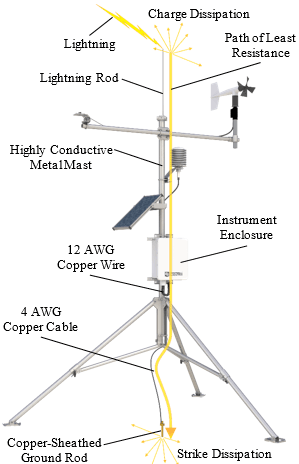
(Click image to expand/collapse display)
All critical inputs and outputs on the data logger are ![]() ESD Electrostatic discharge. protected. To be effective, the earth ground lug must be properly connected to earth (chassis) ground.
ESD Electrostatic discharge. protected. To be effective, the earth ground lug must be properly connected to earth (chassis) ground.
Communications ports are another path for transients. You should provide communications paths, such as telephone or short-haul modem lines, with spark-gap protection. Spark-gap protection is usually an option with these products; so, request it when ordering. Spark gaps must be connected to earth (chassis) ground.
For detailed information on grounding, see Grounds.